TWDNZ
TECHNOLOGY
At TWDNZ, we revolutionise drone inspections with advanced sensors and innovative software. Our technology ensures comprehensive, accurate results through meticulous planning, data collection, processing, and analysis. With cutting-edge tools and platforms, we deliver precise, reliable inspections, providing critical insights for informed decision-making. Explore how TWDNZ empowers your projects with our state-of-the-art technology.
SENSORS
Standard cameras for visual inspections.
Detect heat anomalies indicating potential issues.
Creates detailed 3D models of structures and terrain.

Analyse material properties and detect issues not visible to the naked eye
For non-destructive testing (NDT) and detecting structural defects.
High-Resolution RGB Cameras
High-resolution RGB (Red, Green, Blue) cameras capture images in high detail and colour fidelity, utilizing three colour channels to represent images similar to how the human eye perceives colour. The RGB Camera is an essential and most used tool on our UAV’s.

They provide high-quality images and videos, essential for professional photography, filmmaking, and content creation.
Used in fields like biology and astronomy to capture detailed images for analysis and study.
High-resolution cameras enhance image clarity, making it easier to identify faces, license plates, and other details.
Used to inspect products for defects and ensure quality control in manufacturing processes.
Provide detailed environmental mapping, crucial for creating immersive experiences.
Thermal cameras
Thermal cameras, also known as infrared cameras, detect infrared radiation (heat) and convert it into an image that can be analysed. These cameras are useful in various applications.

Detect heat signatures of intruders or pests in complete darkness, fog, or smoke.
Identify overheating equipment, electrical faults, or insulation issues.
Detect heat leaks, moisture intrusion, and structural issues in buildings.
Locate hotspots in fires and identify trapped individuals through smoke.
Study thermal properties of materials and systems.
LiDAR
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a remote sensing method that uses laser light to measure distances to objects. It creates precise, three-dimensional information about the shape and surface characteristics of the Earth and other objects. Here’s an overview of LiDAR and its applications.
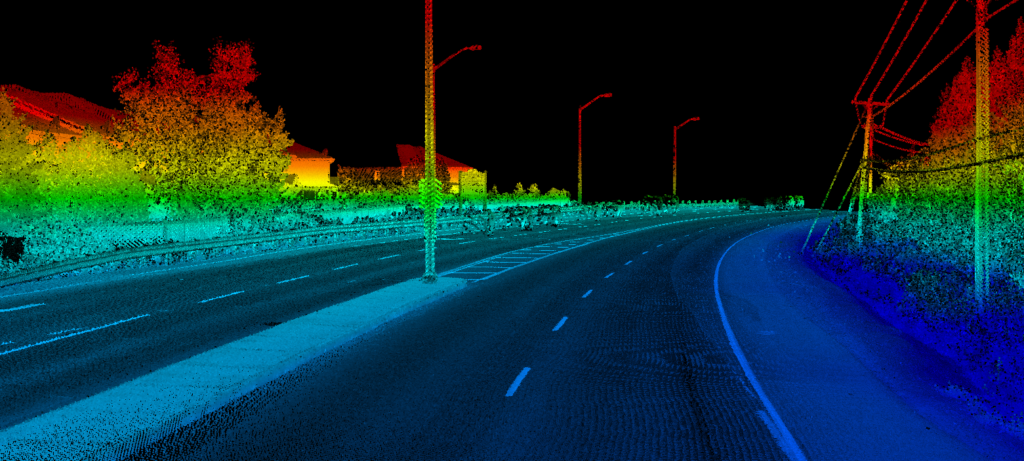
Used to create high-resolution maps of terrain and surface features.
Assesses forest structure, biomass, and health by analyzing tree canopy and ground surface data.
Maps urban environments for infrastructure planning, construction, and maintenance.
Reveals hidden structures and features beneath dense vegetation without disturbing the site.
Maps coastal zones and floodplains to monitor erosion, plan flood defenses, and manage resources.
Measures stockpile volumes, maps mine sites, and monitors environmental impact.
Analyses crop health, soil properties, and topography for precision farming.
Assesses damage and plans recovery efforts after natural disasters like earthquakes, hurricanes, and floods.
Multispectral Sensors
Multispectral and hyperspectral sensors are advanced imaging systems that capture data across multiple wavelengths of light, beyond the visible spectrum. They are crucial for applications requiring detailed spectral information.
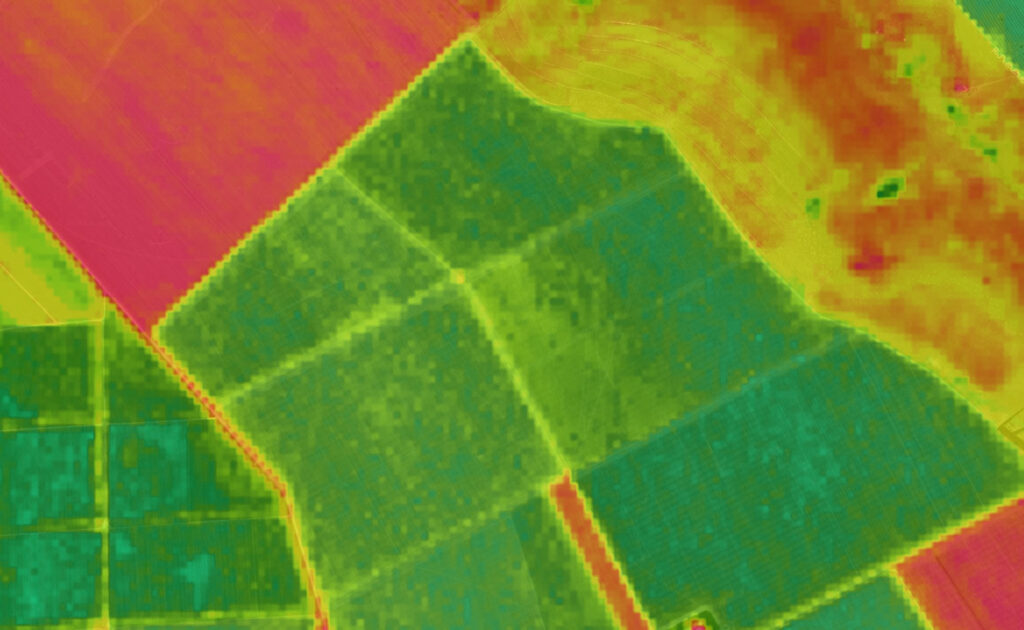
Monitor crop health, soil properties, and irrigation needs. Identify plant stress and disease.
Track changes in vegetation, water quality, and land use. Detect pollutants.
Assess forest health, monitor deforestation, and manage forest resources.
Map mineral deposits and study soil composition.
Monitor water bodies, assess turbidity, and detect algal blooms.
Analyse land cover and land use changes in urban areas.
WORKFLOW
Our workflow involves several stages, from planning and preparation to data analysis and reporting. Here’s an overview of a typical UAV operations workflow for most applications
SOFTWARE
Photogrammetry Software: Pix4D, DroneDeploy, Agisoft Metashape for processing images and creating 3D models.
Inspection Analysis Software: Skydio, Kespry, and Airware for specific inspection needs, including defect detection and reporting.
Data Management and Visualization: Platforms like Propeller Aero, Site Scan, and ArcGIS for managing, visualizing, and sharing inspection data